Global Automotive & Transportation Industry Outlook, 2025
An in-depth analysis of key trends, market dynamics, and growth opportunities shaping the Global Automotive and Transportation industry in 2025.

Author: Swarup Sahu
Introduction to the Automotive & Transportation Industry
The Automotive & Transportation sector includes the industries engaged in the design, production, and distribution of vehicles, along with the systems that help the movement of people and goods. Together, the automotive and transportation industries form essential pillars of the global economy, driving connectivity and commerce by facilitating the flow of people, products, and services. Automotive & Transportation sector are deeply interconnected, with automotive serving as an important segment within the broader transportation landscape, which generated revenue of $14.2 trillion in 2024. The industry depends on extensive supply chain networks that include oil and steel and plastics and rubber while simultaneously constructing worldwide roads, fuel stations and transportation infrastructure.
The automotive and transportation industry has evolved through distinct phases of innovation and expansion. The late 19th century marked the beginning of gasoline-powered vehicle development, which advanced rapidly after Henry Ford implemented the assembly line in 1913, making cars affordable for general public. The sector expanded worldwide after World War II due to the increasing market needs and better infrastructure development.
Today, the auto industry is one of the largest and most influential markets worldwide. It plays a crucial role in trade, jobs, and technology. The industry-maintained stability during the past decade but currently faces substantial changes due to sustainability initiatives and digital transformation. The world has started a major transition toward electric vehicles (EVs) as its primary transportation choice. The International Energy Agency (IEA) reports that electric vehicle sales surpass 17 million units worldwide in 2024 and forecasts 22 million units for 2025 while predicting 60 million units annually by 2030. The market expansion results from consumer demand and supportive government policies.
In addition to electrification, several key trends are reshaping the automotive and transportation industry. Autonomous vehicles are gaining traction, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, sensor technologies, and safety systems. American Academy of Actuaries reports that the global market for automated vehicles is expected to grow from 0.1% of vehicle registration share in 2021 to 12% or nearly 101 million units in 2030. Further the shared mobility is expanding as consumers increasingly prefer flexible, service-based transportation options over private ownership. In the three largest markets China, Europe, and the United States the shared mobility industry is expected to value at $54.2 billion in 2025 which is account for 6% of global passenger vehicle kilometers traveled (VKT), and this share is projected to rise substantially, reaching up to 35% by 2040. Collectively, these developments, along with government support, stricter emission rules, and investments in infrastructure, are leading the industry toward a more efficient, connected, and sustainable future.
Looking ahead, the automotive and transportation industry is expected to reach $21.4 trillion by 2035. This growth will be fueled by the global shift toward electric and autonomous vehicles. It will also be driven by rising usage of connected and shared mobility solutions, improvements in smart transportation infrastructure, and government policies that support sustainability and reducing emissions.
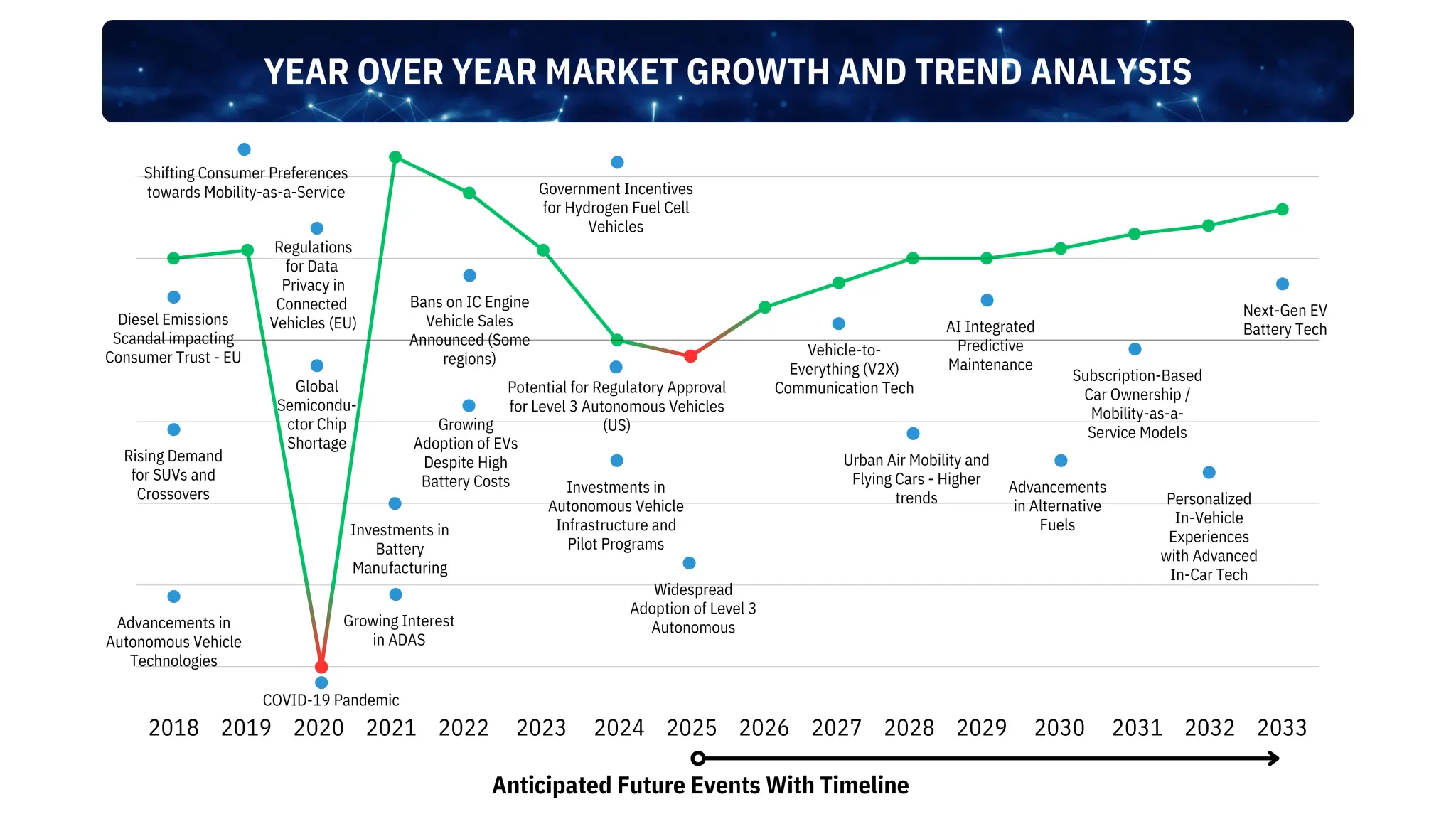
Automotive industry growth pattern showing key milestones such as COVID-19 disruption and EV transformation.
Market Landscape and Economic Importance
The automotive and transportation industry is a cornerstone of the global economy, driving industrial growth, trade, and societal development. The automotive sector generates 3% of worldwide GDP while China and India reach 7% of their national GDP through their expanding automotive industries. The sector creates employment for millions of people while driving infrastructure development of roads, ports and smart cities and it boosts productivity, service accessibility and life quality.
The automotive industry shows distinct regional strengths because of historical development and modern technological progress. The North American region maintains its position as a technological leader through its advancements in electric vehicles, autonomous driving systems and connected mobility technologies. The United States serves as a home base for General Motors, Ford and Tesla as well as technology companies that focus on electric vehicle development, autonomous systems and smart mobility solutions. As per International Energy Agency (IEA), the U.S. electric vehicle market achieved 1.6 million unit sales in 2024 which represented 10% of total light-duty vehicle sales a significant increase from 7.6% in 2023. Federal and state policies such as EV tax incentives, emission reduction regulations, and infrastructure funding for charging networks support domestic growth while enhancing the U.S.'s strategic position in the global automotive & transportation landscape. The country maintains its position as a leader in future mobility solutions through investments in AI autonomous systems, advanced battery technologies and smart transportation platforms.
Europe maintains a strong position in the world due to its exceptional engineering capabilities and premium automotive production standards. Germany, France, and Italy combinedly contribute a significant share of global vehicle production and are leading the development of hybrid powertrains, industrial automation, and integrated connected vehicle ecosystems. The EU Green Deal and strict CO₂ emission rules within Europe's regulatory framework push companies toward sustainable transportation solutions. The European Union Green Deal targets 30 million zero-emission cars and 80,000 zero-emission lorries to operate on European roads by 2030. The EU Chips Act further enhances European automotive technology competitiveness through semiconductor-dependent systems. Germany demonstrates its dedication to technological progress and environmental sustainability through its industrial robotics adoption and EV infrastructure investments.
In the Asia-Pacific region, China, Japan, and South Korea dominate global vehicle production and technology adoption. China has emerged as the world's largest EV market, supported by government subsidies, local manufacturing capabilities, and growing consumer demand for clean mobility. Japan and South Korea excel in hybrid and electric vehicle technologies, battery production, and automotive electronics. South Korea's EV market is projected to reach a 20% share of total vehicle sales by the end of 2025, driven by government policies aimed at achieving carbon neutrality, including the expansion of charging infrastructure, tax incentives, and technological advancements. Simultaneously, emerging markets such as India, Vietnam, and Indonesia are gaining strategic importance as investment destinations for vehicle assembly, EV infrastructure, and connected mobility initiatives. India's automotive sector benefits from government programs promoting EV adoption and domestic manufacturing, while Vietnam is establishing itself as a regional hub due to favorable labor costs and strategic trade agreements.
The industry functions as a vital support system for sectors which demonstrate rapid expansion. The development of electric and autonomous vehicles requires semiconductors together with modern materials and artificial intelligence-based software systems. The use of IoT technology and telematics systems with data analysis tools enhances supply chain operations in logistics and freight operations. The sector supports worldwide decarbonization efforts through its adoption of renewable energy systems which include hydrogen and battery-electric transportation solutions. The automotive and transportation industry enables global economic growth through innovation and competitive advantage and productivity enhancement and maintains its position as a vital transformative force in the economy.
Segmentation of The Automotive & Transportation (A&T) industry
The Automotive & Transportation (A&T) industry operates as a large interconnected system which drives worldwide economic expansion and industrial progress and technological breakthroughs. The A&T industry operates through four distinct segments which include Automotive & Mobility, Transportation & Logistics, A&T Technology and A&T Peripherals to fulfill different market requirements while supporting worldwide mobility, trade and infrastructure construction.
The four segments operate as a unified system which enables the global A&T industry to maintain its position as a fundamental driver of economic advancement. The combination of modern technology, sustainable methods and intelligent infrastructure systems drives ongoing expansion and innovation and market competitiveness throughout the industry. The Automotive & Transportation industry drives global economic growth through its support of electric mobility, autonomous vehicles and connected logistics systems.
Automotive & Mobility
The Automotive & Mobility sector functions as the fundamental foundation of the industry as it includes passenger vehicles, commercial vehicles, electric and hybrid vehicles as well as emerging mobility solutions like shared and autonomous vehicles. The worldwide automotive market generated more than USD 4.8 trillion in revenue during 2024, reflecting strong demanding for both standard and electric vehicle. The industry experiences a transformation through technological advancements which include ADAS systems, connected vehicle platforms and sustainable power systems that create safer and more environmentally friendly mobility solutions. The automotive industry demonstrates worldwide reach through its production bases, electric vehicle adoption and next-generation mobility technology development in North America and Europe and Asia-Pacific regions.
Transportation & Logistics
The Transportation & Logistics sector supports worldwide trade operations by linking freight services, passenger transport, warehouse facilities and last-mile delivery systems. The global logistics industry reached USD 8.7 trillion in value during 2024 due to the rising e-commerce activity, urban population growth and improved infrastructure development. The combination of fleet management advancements with telematics, AI-based route optimization and electric transport fleet adoption leads to better operational performance while reducing costs and carbon emissions. Further, investments in ports, railways, highways, and smart transport corridors strengthen this segment, enabling seamless domestic and international connectivity.
A&T Technology
The A&T Technology sector provides digital solutions, hardware and software elements which power modern vehicles and transportation systems. The technology sector within the industry focuses on developing advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), telematics and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, AI-powered autonomous driving platforms and connected mobility infrastructure. The segment reached USD 182.6 billion sales in 2024, reflecting the critical role of digital innovation in transforming mobility. The combination of AI with IoT and data analytics in vehicles and transportation networks creates efficient and safe operations while making the industry the leader in smart mobility solutions.
A&T Peripherals
A&T Peripherals encompasses essential components and products which support automotive and transportation operations, including tires, batteries, sensors, electronics and charging systems. The segment maintains the operational reliability, safety and efficiency of vehicles and transportation systems. The global market for automotive peripherals reached USD 514.8 billion in 2024, highlighting its strategic importance across all vehicle categories and transport systems.
Key Growth Drivers
The global Automotive & Transportation (A&T) industry is experiencing accelerated transformation, driven by technological innovation, sustainability mandates, and evolving mobility trends. The industry's expansion stems from four major forces: the electrification of vehicles, the rise of connected and autonomous systems, rapid logistics and mobility evolution, and the integration of advanced materials and manufacturing automation. These dynamics are reshaping how vehicles are designed, produced, and used, redefining the global competitive landscape.
Electrification and EV Market Expansion
The electrification of mobility remains the most powerful catalyst for growth in the Automotive & Transportation industry. IEA reports that, global electric vehicle (EV) sales surpassed <strong>17</strong> million units in 2024, accounting for nearly <strong>20%</strong> of total vehicle sales, up from <strong>4%</strong> in 2020. The EV market is projected to exceed <strong>$1.2</strong> trillion by 2030, with a CAGR of <strong>17-18%</strong> during 2025–2030. China continues to lead the transition, contributing over <strong>55%</strong> of global EV demand, followed by Europe and North America.
Government policies play a crucial role, the EU aims to ban internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle sales by 2035, while India targets <strong>80</strong> million EVs on the road by 2030. Simultaneously, rising oil prices and tightening carbon regulations accelerate fleet electrification across public and commercial transportation. The growing adoption of EVs also stimulates demand for battery technologies, charging infrastructure, and semiconductor-based power systems, reinforcing the vertical integration between automotive, energy, and electronics sectors.
Connected, Autonomous, Shared, and Smart (CASS) Mobility
The industry's digital transformation is defined by connected and autonomous technologies. By 2024, more than 75% of new vehicles sold globally featured embedded connectivity or telematics systems. The global connected car market exceeded $355 billion by 2030 and is forecasted to grow at a 15% CAGR between 2025-2030, driven by 5G integration, AI-based predictive maintenance, and over-the-air software updates.
Autonomous driving technologies are rapidly advancing Level 3 systems are now commercially available in Japan, Germany, and select U.S. states, while fully autonomous Level 4 trials are expanding in urban zones. The global autonomous car market is projected to exceed <strong>$17.5</strong> billion by 2030, with logistics fleets and robotaxis leading adoption. These trends collectively redefine mobility as a service (MaaS), enhance road safety, and enable data-driven fleet management.
Logistics Modernization and Smart Transportation Infrastructure
The Transportation & Logistics segment underpins global trade by integrating freight movement, passenger transit, warehousing, and last-mile delivery systems. Global logistics spending exceeded <strong>$10 </strong>trillion in 2024, representing nearly <strong>10%</strong> of global GDP, reflecting its immense economic significance. The ongoing digitalization of logistics including real-time tracking, AI-driven routing, and automated warehousing enhances supply chain resilience.
Emerging smart transportation infrastructure initiatives, such as intelligent traffic management systems and electronic toll collection, are transforming urban mobility. Governments across Europe and Asia are investing heavily in multimodal networks and electrified freight corridors. For instance, the EU's 'Connecting Europe Facility' has allocated nearly $39.3 billion for cross-border infrastructure development, supporting seamless logistics and passenger connectivity across regions.
Advanced Materials, Lightweight Design, and Manufacturing Automation
To meet emission targets and efficiency goals, automakers are increasingly adopting lightweight materials such as aluminum, carbon fiber composites, and high-strength steel. The global market for automotive lightweight materials surpassed <strong>$126</strong> billion in 2030 and is expected to grow at a <strong>6%</strong> CAGR between 2025-2030. Weight reduction directly contributes to fuel efficiency and EV range optimization, while also enabling improved safety performance.
Simultaneously, advanced manufacturing practices such as 3D printing, robotics, and digital twins are revolutionizing vehicle production. Over <strong>50%</strong> of global automotive OEMs have implemented smart factory initiatives integrating robotics and AI-driven quality control. This automation enhances precision, reduces costs, and accelerates time-to-market. The synergy between advanced materials and manufacturing automation is redefining production economics, ensuring sustainability and scalability in the evolving automotive ecosystem.
Challenges & Restraints
The Automotive & Transportation sector undergoing a fundamental industry shift due to the combined impact of electrification, automation, connectivity, and environmental sustainability requirements. The industry faces multiple interconnected obstacles which include supply chain instability, high production costs, strict regulations and insufficient skilled workers across different geographic region. The existing barriers in the market sector affect profit margins as well as limit OEMs' ability to transition toward next-generation mobility solutions.
Supply Chain Volatility & Raw Material Dependence
The automotive supply chain operates through extensive global networks which face continuous threats from political instability and logistical disruptions. The pandemic together with semiconductor shortages revealed how dependent the industry remains on restricted suppliers operating from specific geographic areas. The majority of essential automotive semiconductor production takes place in East Asia where <strong>75%</strong> of total output occurs while EV battery materials like lithium and cobalt and nickel originate mainly from China and the Democratic Republic of Congo and Indonesia.
The Russia-Ukraine conflict interrupted the supply of palladium and neon gas which serve as crucial materials for both catalytic converters and chip manufacturing. These disruptions caused global vehicle production losses exceeding <strong>10 </strong>million units between 2021 and 2023, extending lead times for EVs and premium models. To counter this, automakers are localizing supply chains, building regional battery plants, and entering long-term mineral procurement partnerships. However, diversification raises short-term costs and creates operational complexity.
High Capital & Infrastructure Demands
The industry faces significant capital strain as it transitions from internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles to electrified and autonomous platforms. The establishment of a new EV manufacturing facility requires between USD <strong>2-4</strong> billion in investment while lithium-ion cell production facilities need investments of USD <strong>5-7</strong> billion. Moreover, charging infrastructure expansion remains uneven requiring over USD <strong>400</strong> billion in global investment by 2030 to meet EV adoption targets.
The development of transportation infrastructure including roads and smart traffic systems and public transit electrification requires substantial funding from both public and private sectors. The expenses from production extend beyond manufacturing costs because companies need to invest in digital twin systems and robotics, workforce training and retraining programs. The limited availability of capital restricts new market entries while forcing established OEMs to maintain a balance between their innovation investments and their cost management efforts.
Regulatory Complexity & Sustainability Pressure
The automotive sector faces growing regulatory control which focuses on environmental emissions, product safety and data protection requirements. The EU's "Fit for 55" mandates a 55% reduction in CO₂ emissions by 2030, while the U.S. EPA plans to enforce electric vehicle standards that will make 67% of new car sales electric by 2032. The current regulatory requirements force manufacturers to speed up their transition to electric vehicles but the existing infrastructure and customer readiness levels do not match the established deadlines.
Additionally, sustainability expectations extend across the full lifecycle from raw material extraction and battery recycling to Scope 3 emissions disclosure. The EU Battery Regulation, ISO 14083 logistics carbon reporting and digital product passports standards create both administrative and technological hurdles for companies across the globe.
Key Opportunity
The automotive and transportation industry is evolving rapidly, creating wide-ranging opportunities through vehicle electrification, autonomous technologies, and connected mobility solutions. Growing emphasis on sustainability, smart infrastructure, and advanced manufacturing is reshaping global supply chains and business models. Expanding adoption of electric vehicles, intelligent transport systems, and mobility-as-a-service platforms continues to unlock new avenues for innovation, partnerships, and long-term growth.
Global Partnerships and Strategic Investments
The global Automotive & Transportation industry is entering an accelerated investment phase, with cumulative capital spending expected to exceed USD <strong>3.5</strong> trillion between 2024 and 2032 across electric vehicles, logistics, and infrastructure modernization. The automotive industry partners with technology companies, energy providers and government entities to build electric vehicle production facilities and digital mobility networks.
Major example includes, Hyundai's <strong>$12.6</strong> billion EV production ecosystem in Georgia (U.S.) and Volkswagen's <strong>$180</strong> billion decarbonization investment plant through 2030 and China's <strong>$72</strong> billion smart transport corridor development. The strategic alliances between original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), battery producers and semiconductor suppliers create vertical integration which decreases production costs and builds supply chain stability for the future. The partnerships between companies enable them to build new manufacturing sites worldwide while creating modern mobility systems that support regional economic development.
Sustainability and Circular Mobility
Sustainability has become a central strategic opportunity rather than a compliance requirement. The automotive industry invests in circular economy systems which focus on battery recycling, green manufacturing, lightweight material retrieval and carbon emission-free logistics. The battery recycling market alone projected to reach more than <strong>$35</strong> billion in value by 2030, driven by rising end-of-life EV volumes.
Companies including BMW, Tesla and BYD, operate their own recycling and reuse systems to decrease their dependence on rare earth materials and maintain stable raw material expenses. The electrification ecosystem receives hydrogen mobility as a supporting element because Japan and South Korea intend to deploy more than one million hydrogen vehicles by 2035. Similarly, the sustainability initiatives create profitable business opportunities that enable automakers to generate long-term value through efficient resource management and circular production systems.
Digital Mobility and Data-Driven Ecosystems
The combination of software technology with connectivity and analytics capabilities has established a new revenue opportunity for the A&T industry. The connected car market reached USD <strong>80 </strong>billion in 2024 as automotive companies and service providers use telematics, predictive maintenance and AI-based mobility services. Subscription-based vehicle features, autonomous fleet analytics, and mobility-as-a-service (MaaS) platforms are reshaping how value is generated post-sale. For example, General Motors projects over USD <strong>25</strong> billion in annual digital service revenues by 2030, reflecting the industry-wide shift from one-time vehicle sales toward recurring digital income streams. The global automotive economy now faces a profitable and enduring business opportunity through this fundamental market transformation.
Competitive Landscape
The global automotive industry in 2024 reflected resilience and steady recovery amid macroeconomic and supply chain pressures. According to the market data, Volkswagen Group and Toyota continued to dominate the market, maintaining leadership positions supported by strong brand portfolios and expanding EV product lines. Volkswagen recorded marginal growth driven by stable demand in Europe and China, while Toyota benefited from hybrid vehicle popularity and cost efficiency in global production networks.
General Motors, BMW Group, and Mercedes-Benz Group showed moderate performance, sustaining revenue growth through strong North American and European sales but facing challenges from rising input costs and slower EV adoption rates. Stellantis reported a revenue decline compared to 2023, reflecting weaker demand in key European markets and delayed electrification initiatives. BYD emerged as one of the fastest-growing players, supported by surging demand for electric vehicles in Asia and global market expansion. In contrast, Tesla experienced a revenue decline, mainly due to price cuts and intensifying competition in the EV segment. Overall, the top manufacturers demonstrated adaptability through diversification, digitalization, and electrification strategies, positioning themselves for long-term competitiveness in an evolving global mobility ecosystem.
| Major Companies | 2024 | 2023 |
|---|---|---|
| Volkswagen Group | 351.4 | 348.8 |
| Toyota | 297.9 | 264.4 |
| General Motors | 171.6 | 157.7 |
| stellantis | 183.1 | 221.3 |
| BMW Group | 166.3 | 181.5 |
| Mercedes-Benz Group | 157.6 | 164.9 |
| BYD | 108.1 | 85.1 |
| Tesla, Inc. | 77.0 | 96.7 |
| Porsche | 53.1 | 54.2 |
Note: *Sources – Annual Reports All figures are in USD Billion